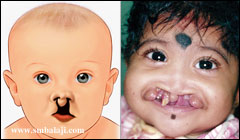
Classification of Cleft Lip and Palate
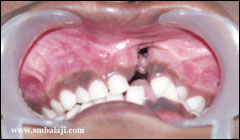
1. Cleft can occur either in the lip, palate or both. The cleft of both the lip and palate mostly involves the upper alveolar (teeth bearing portion of the jaw) bone.
2. A cleft lip can be either unilateral (one-side only) or bilateral (both sides).
3. Cleft lip can either be incomplete (mild notching of the lip) or complete (large gap from lip to nose).
4. Cleft palate can either be Cleft of the Hard Palate- cleft in bony portion of roof of the mouth, Cleft of the Soft Palate- in the soft, muscular part of the palate, behind the hard palate or Cleft of both the Hard and Soft palates including the Uvula (soft tissue projection from middle of soft palate).
Submucous Cleft Palate - This cleft occurs in the tissues beneath the mucous membrane that covers the palate. Hence it is often called the “invisible cleft”. This cleft is detected only when the child has a difficulty in speaking.


-cleft-lip.jpg)