Forehead Injuries
Forehead region is the most vulnerable area of the head and forehead bone fractures are very common. Special x-rays called CT scans are used to evaluate fractures and brain involvement and to help plan the surgical reconstruction procedure. Depending on the severity of the fractures, reconstruction is done. The ultimate aim is to achieve as good a functional and cosmetic outcome as possible.
Frontal sinus fracture: The frontal bone or bone of the forehead lodges air-filled space cavities called the frontal sinus. During injuries of the forehead, the walls of the frontal sinus may be fractured. These cases necessitate accurate diagnosis, avoidance of short and long term complications, precise treatment and return of normal sinus function.
Trauma to the temporal area (sides of the forehead) may be critical. As the area involves the ears, complications from such fractures lead to hearing loss or vertigo (feels like the room is spinning around). Although the vertigo may resolve over time, the hearing loss, most of the time, if untreated or inadequately treated, persists. As this part of the face includes the nerves that supplies the entire facial muscles, damage in this area may culminate as Facial Nerve palsy or loss of expression and control of facial expression.
All these conditions need to be properly assessed. Appropriate treatment and therapies need to be instituted based on the extent of damage, duration of swelling, extent of loss of function and other vital parameters.
Seen here are photographs of 3 patients who suffered serious injuries to their forehead and were successfully treated in our hospital.
CASE I:
-
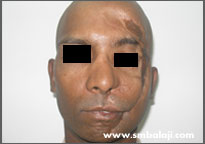
A patient who suffered severe injury in an accident
-

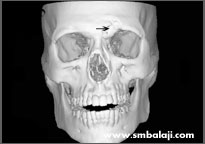
3D CT scan showing bony deficit of the forehead bone
-
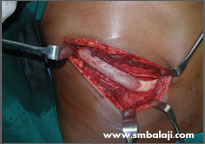
Graft harvested from the patient's rib
-
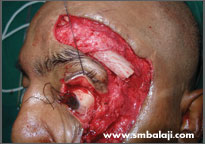
Upper rim of eye bone and forhead bone reconstructed with the graft
-
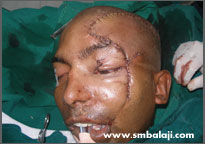
Immediately after surgery
-
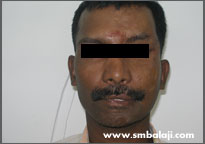
Few days after surgery
The patient had met with a serious accident and had sought treatment elsewhere. The inappropriate treatment resulted in a face deformity. The forehead bone and eye socket bone on the left side of his face was deranged and he had an unsightly scar.
He sought the expertise of Dr. S.M. Balaji for specialized treatment and expert care. A CT scan was taken to gauge the extent of the defect. A graft from his rib was harvested and used to reconstruct his left forehead and eye socket region. Following successful reconstruction of the skeletal framework, his appearance improved dramatically.
CASE II:
-
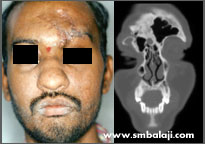
Forehead bone fracture, CBCT image of fracture
-
CT image showing fracture of the frontal sinus wall and orbital rim of forehead bone
-
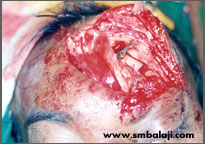
Fracture of the frontal sinus wall treated by fixing bone plate
-
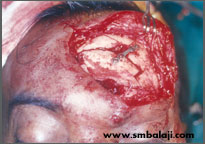
Fixation of the frontal sinus wall using bone plate
-
Good healing following surgery
A man suffered an injury to his forehead. An advanced 3D Cone Beam CT scan was taken to see the extent of the trauma. After ruling out damage to the brain, the fractured bone segments were fixed with bone plates.
CASE III
-
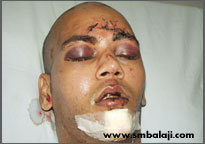
Fracture of the forehead bone with severe swelling around the eyes
-
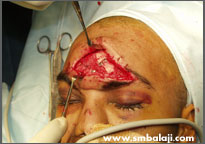
Fractured bones fixed with bone plates during surgery
-
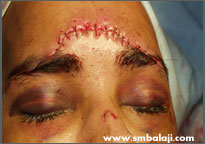
Immediately after surgery, the wound is closed in layers
A young man was given immediate first aid elsewhere before he was referred to us with serious facial injuries. A CT scan showed the exact extent of his wounds. The fractured bones of the walls of the frontal sinus in the forehead region were stabilized and treated with bone plates.
