Pre-Prosthetic Surgery
Sometimes surgical modifications of the jaw bone and soft tissues are required to enable the placement of a well-fitting, comfortable and aesthetic dental prosthesis such as dentures or dental implants. This preparation is referred to as pre-prosthetic surgery.
It is important that the bony ridge and soft tissues be of proper size and shape before placing the prosthesis. To achieve this, one or more of the following procedures might be needed
- Bone smoothing and reshaping (alveoloplasty)- irregular or sharp bone ridges are smoothened off
- Bone grafting – this is required to “fill in” the bony defects. When there is missing teeth, jaw bone tends to shrink over time. There may not be sufficient bone to place dental implants or prosthesis. Or bone defects may occur due to gum disease. Bone grafting is a procedure to rebuild bone in the bone deficient areas of the jaw. For this, bone may be harvested from other parts of the jaw, patient’s rib or bone substitutes may be used.
- Removal of excess bone (exostoses)- large and irregular chunks of excess bone may need to be removed to allow denture to fit properly.
- Adding, removing or reshaping the soft tissues- the soft tissues inside the mouth may require to be surgically corrected to have a well-fitting, stable denture. Excess soft tissue may require to be removed or some tissues may need to be repositioned to ensure a successful prosthesis. Soft tissue grafting may sometimes be required.
CASE I
-
-image-of-the-lower-jaw-showing-mandibular-tori-(exostoses).jpg)
3D Cone Beam CT (CBCT) image of the lower jaw showing mandibular tori (exostoses)
-
-image-of-the-lower-jaw-showing-mandibular-tori-(exostoses)-.jpg)
3D Cone Beam CT (CBCT) image of the lower jaw showing mandibular tori (exostoses)
-
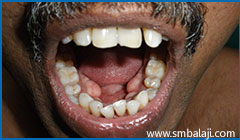
Clinical photograph showing the tori
-
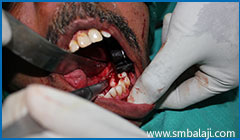
Tori surgically excised from the lower left jaw region
-
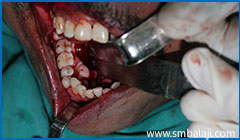
Tori surgically excised from the lower right jaw region
-

A portion of the excised bone excess
CASE II
-
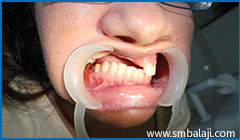
Severely insufficient bone in missing teeth region of upper jaw and slanting bite
-
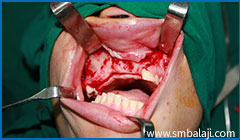
Deficient region surgically exposed
-
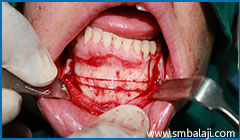
Mandibular segmental subapical osteotomy - excess bone removal from left lower jaw to correct slanting bite
-
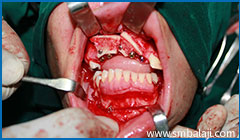
Implant placement in upper jaw after bone grafting with excess bone from lower jaw
CASE III
-
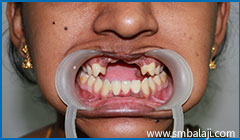
Missing upper front teeth with insufficient bone and altered alignment of upper and lower jaw
-
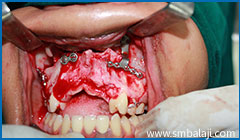
Le Fort I maxillary osteotomy and upper jaw advancement
-
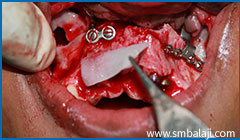
rhBMP-2 placed to stimulate new bone formation and implants placed
-
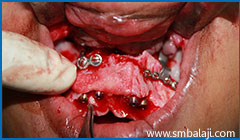
rhBMP-2 will stimulate new bone formation reinforcing the bone deficient region
-
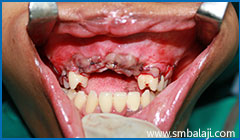
Upper jaw adequately advanced and brought into more favourable position in relation to lower jaw
-
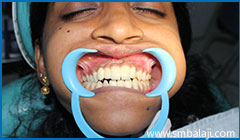
After completeion of prosthetic rehabilitation with ceramic crowns and correct teeth alignment
